Conversational AI, basically it’s about getting machines talk to us, like a real person almost in natural language. These systems use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to understand questions and give answers. Think about it, you can speak with these systems instead of typing commands, you might have used a chatbot online. These are examples of conversational AI. It powers everything from simple FAQ bots on websites to advanced tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and deepseek. That’s how they decipher what we’re saying, Machine learning (ML), helps them learn and improve over time.
Topics Covered
Table of Contents
What Is Conversational AI?
You’re probably hearing a lot about “Conversational AI” these days. It is a software that can understand and respond to you in human language. It includes chatbots and voice assistants. Unlike old preprogrammed bots that only follow scripts, we are talking about modern and much smarter chatbots, conversational AI learns from tons and tons of data. It uses deep learning to process text or speech, figure out intent, and craft a reply. Pretty cool, behind the scenes, it relies on two key parts:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): This is how the AI figures out what you mean. It breaks down your sentences, finds key words you used in your talk, and guesses your intent. For example, if you ask “Where is my car key?” the system recognizes you want tracking info.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG): This is how the AI crafts and gives you a reply. Once it knows what you want, it uses a language model to write a helpful answer about your question. It tries to sound natural and clear. Advanced systems use pre-trained models like GPT or BERT.
If you want to Learn AI read this beginner guide about AI and ML Learning
By combining NLU, NLG, and dialogue management, It can answer questions, provide recommendations, automate transactions, or just chat informally. That’s great.
How Does Conversational AI Work?
Working of conversational AI:
- User Input: If you type or speak a sentence, like “Book me a hotel room in Istanbul for next week.”
- Processing: The AI uses speech recognition and NLU to interpret the input. It detects meaning, context, and any important details (dates, location, etc.).
- Intent & Entities: The system identifies the intent (“book hotel”) and extracts entities (city = Istanbul, date = next week).
- Backend Action: Based on our intent, it might search a database, call an API, or run a booking program. This is the “robot” part handling your request.
- Response Generation: Using NLG, it formulates a response like “I found hotels in Istanbul from July 20 to 25. Which one would you like to book?”
- User Follow-up: You respond, and the cycle continues until the booking task is done.
Modern systems also use large language models (LLMs). The key is data. Conversational AI improves by learning from our past conversations. Each user interaction helps it get better at understanding slang, accents, or new topics. It can also be designed to switch context smoothly, remember previous questions, and even handle minor mistakes or typos made by us.
Types of Conversational AI
There are several kinds of conversational AI, based on how you interact:
- Chatbots (Text): These are usually found on websites, apps, or messaging platforms. You type questions or click buttons. Examples include customer service bots, sales assistants on e-commerce sites, and even simple game or trivia bots.
- Voice Assistants (Voice): These use speech recognition so you talk out loud. Examples are virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and Cortana. Voice bots also power phone call systems (interactive voice response).
- Social Bots: Some conversational AI live on social networks (Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, and Telegram). Companies use them to send updates or answer FAQs in chat apps.
- Hybrid Bots: These can handle both text and voice, and often include other features. For example, a smart home assistant might use voice at home and chat on your phone.
Each type uses the same basic tech but tuned for its interface. For example, voice bots add speech-to-text and text-to-speech modules.
Common Examples
Here are a few familiar conversational AIs:
- ChatGPT: A powerful text-based AI by OpenAI. People use it to get information, write drafts, or even code. It’s known for very human-like answers.
- Siri (Apple), Alexa (Amazon), Google Assistant: These voice assistants live on phones and smart speakers. They answer questions, control smart home devices, set reminders, and more.
- Customer Service Bots: Many companies (banks, telecoms, airlines) have chatbots on their websites or apps to answer questions about orders, accounts, or troubleshooting.
- Virtual Agents in Apps: Apps like banking or travel booking apps often have an embedded bot or live chat option.
- Social Media Bots: Some brands use bots on Messenger, WhatsApp, or Twitter to engage customers or send news.
Why Conversational AI Important
Conversational AI is powerful because it meets users where they talk. Instead of navigating menus or reading manuals, people can just ask or tell the system in plain language. Here’s why businesses and users care about it:
- 24/7 Availability: A chatbot never sleeps. It can answer basic customer questions at any time, even at 3 AM. This means faster help for users and lower wait times.
- Scalability: A single bot can talk to thousands of users at once. In contrast, a human agent can only help a few people at a time. This massively scales customer support without adding staff.
- Cost Savings: Automating routine tasks with AI reduces labor costs. Companies estimate savings in the billions. By 2025, some experts predict chatbots could reduce service costs by around $11 billion globally.
- Personalization: Modern bots can remember user preferences and history. This means they give personalized responses. For example, a retail chatbot might suggest products based on your past purchases.
- Engagement and Sales: Chatbots can proactively engage customers. They might suggest deals or help close sales. In fact, studies show 26% of all sales originate from chatbot interactions. That means more than a quarter of buyers ended up purchasing because a chatbot helped them!
- Data and Insights: Conversations generate data. By analyzing chat logs, companies learn what customers ask most, what problems are common, and what products are popular. This feedback loop improves both the bot and overall business strategy.
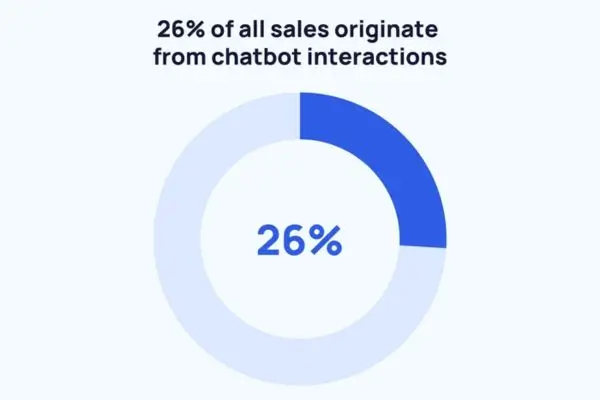
Many companies see big sales boosts from chatbots – 26% of all sales come from chatbot conversations. This chart highlights how significant chatbots are for revenue. By answering questions and guiding buyers, bots help close deals quickly and boost growth.
On the user side, people enjoy quick, text-based interactions. Millennials and Gen Z in particular prefer messaging over phone calls. A survey found over 50% of millennials would rather use a chatbot than wait for a human agent. This trend means websites and apps that don’t have a friendly AI chat option might lose customers to ones that do.
Uses of Conversational AI
Conversational AI is used in many fields. Here are some common use cases by industry:
- Customer Support: Banks, telecoms, e-commerce sites, and utility companies use chatbots to answer FAQs (account balance, bill pay, and order status). This cuts wait times. For example, 90% of businesses saw faster complaint resolution thanks to chatbots. That means most companies resolved customer issues more quickly with AI.
- E-commerce Sales & Marketing: Online stores use bots to recommend products, answer sizing or stock questions, and even complete purchases in chat. They qualify leads (asking interests) and pass hot leads to human sales. Sales teams report that chatbots helped close 35% more deals.
- IT and Internal Helpdesks: Large companies deploy bots to help employees with password resets, ticket status, or HR questions. Internal chatbots lighten the load on support staff and help new hires navigate systems.
- Healthcare: Chatbots can triage symptoms, schedule appointments, send medication reminders, or provide health tips. During the pandemic, many clinics used bots to handle overflow questions about COVID symptoms and vaccine info.
- Education and Training: Virtual tutors can answer student questions, help with practice quizzes, or explain concepts. Language learning apps use chatbots for practice conversations. Corporations use bots to train employees on compliance or product info.
- Finance and Banking: Conversational AI helps with balance inquiries, fraud alerts, loan applications, and more. For instance, a bot might alert you to unusual transactions or guide you through budgeting tips.
- Travel & Hospitality: From booking hotels and flights to providing local tips, travel bots can make planning trips easier. Airlines use them for check-in, flight status, and loyalty program info. Hotels use them for room service or concierge services.
These use cases show that virtually any business can leverage conversational AI. It works globally, in many languages, and adapts to each scenario.
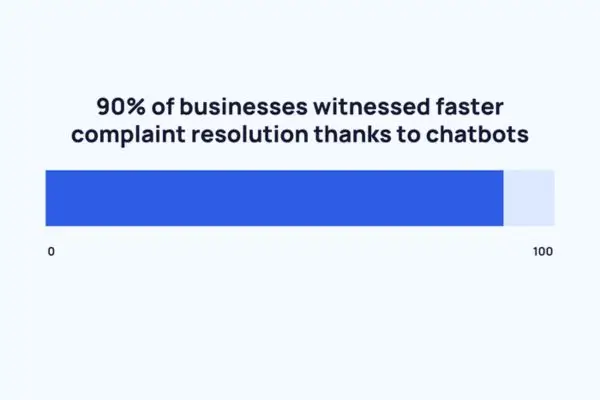
Chatbots make customer support faster – 90% of businesses saw quicker complaint resolution after adding chatbot support. This bar chart illustrates how widely conversational AI improves service. By answering simple issues instantly, bots free human agents to tackle complex problems.
Key Benefits of Conversational AI
Putting the above together, the main benefits of conversational AI include:
- Always-on Service: Bots never take breaks or vacations. Your service is available day and night.
- Instant Response: Bots can reply in seconds. This hugely improves customer satisfaction. Many users expect immediate answers; waiting hurts business reputation.
- Multilingual Support: With global reach, bots can be trained in multiple languages. This means a company can serve users in many countries easily.
- Efficiency & Cost Cut: Automating basic queries reduces the number of questions human agents must handle. Industry reports show bots can reduce average response time by 3× compared to humans. Over time, companies cut support costs significantly.
- Scalability: During peak times (like holidays), bots handle the load without overtime or temp workers.
- Data Collection: Every chat is data. Businesses analyze conversations to find common issues and improve products.
- Consistent Answers: Unlike humans who might give slightly different answers, bots can provide standardized information. This consistency is important for compliance and brand image.
- Engaging Experience: Modern bots can be quite sophisticated, using images, quick-reply buttons, or even personality to make interactions fun.
In short, conversational AI makes interactions more human-like, efficient, and scalable. It helps businesses serve customers better, learn from interactions, and grow revenue.
Overview Table of Conversational AI Use Cases
| Use Case | Example Industry | Key Benefit |
| Customer Support | Banks, Retail, Telecoms | 24/7 help desk; faster issue resolution |
| Sales & Marketing | E-commerce, Finance, Travel | Lead qualification; personalized recommendations |
| IT Helpdesk / HR | Corporate IT, Enterprise | Employee self-service; quick troubleshooting |
| Healthcare Guidance | Telemedicine, Hospitals | Symptom triage; appointment booking |
| Education & Training | E-learning, Corporate Training | On-demand tutoring; interactive learning |
| Banking & Finance | Banks, Insurance | Account queries; fraud alerts |
| Travel & Hospitality | Airlines, Hotels, Tourism | Trip planning; check-in; local tips |
Table: Common conversational AI applications across industries and their main benefits.
This table sums up how conversational AI is applied. Notice how diverse the use cases are – from front-line customer chats to behind-the-scenes employee helpers.
How Conversational AI is built
For tech professionals, it’s worth noting the building blocks of conversational AI:
- NLP/NLU Engines: Tools like Google Dialog flow, IBM Watson Assistant, Microsoft LUIS, and open-source Rasa handle language understanding. They parse input and map it to intents/entities.
- Dialogue Management: This is the “brain” that decides what the bot should say next. It keeps track of conversation history and context. Open source frameworks or custom code manage this logic.
- Machine Learning Models: Many modern bots use pre-trained language models (like GPT, BERT) fine-tuned on specific dialog data. These allow more flexible, human-like replies.
- Integration Layers: Bots connect to backend systems (databases, APIs). For example, a banking bot must securely fetch account info. These integrations require careful API design.
- Channels and Interfaces: Bots can connect to websites, mobile apps, social media (Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp), or voice platforms (phone, smart speakers). Each channel might need specific adaptations (speech recognition vs. text).
- Analytics & Feedback: Successful bots include analytics dashboards and feedback loops. Teams review chat logs and metrics to improve conversation flow and accuracy.
Building a bot often starts with a conversation design phase: mapping out expected dialogues, writing sample scripts, and defining fallback rules. Testing with real users (or user data) is crucial to refine the system. And because language and needs change, maintenance and retraining are ongoing processes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, conversational AI has challenges:
- Understanding Limitations: AI still struggles with complex queries, sarcasm, or ambiguous phrasing. A bot might misinterpret unclear user language. Designing fallback or handoff to humans is important.
- Context and Memory: While advanced models can keep context within a conversation, long-term memory (like recalling a detail from last month’s chat) is still tricky. Systems often have to be engineered specifically for such memory.
- Data Privacy: Chatbots often handle personal or sensitive data (orders, health info, and financial data). Ensuring GDPR, HIPAA, or other compliance is vital. Data breaches could be disastrous. Strong encryption and data policies are needed.
- Bias and Fairness: Training data may have biases. A chatbot could inadvertently give offensive or biased responses. Companies must monitor and fine-tune bots to avoid this.
- Voice Recognition Accuracy: Voice bots must deal with accents, noise, and different languages. Accuracy is improving, but not perfect. Companies often provide easy ways to switch to text or to repeat if misunderstood.
- Human Touch: Some customers still prefer human help, especially for emotional or complex issues. Over-reliance on AI might frustrate those people. Blending AI with human support is often best practice.
- Cost and Maintenance: Building a simple bot is easy, but advanced AI bots can be expensive (from thousands to millions of dollars in development). They also need ongoing updates as language and products change. Poorly maintained bots can give wrong information.
By planning carefully, many of these issues can be mitigated. For example, always give users the option to “talk to human agent” if the bot can’t help. Regularly test the bot with real users to catch problems. And keep human oversight, where real people review conversations to improve the bot’s performance.
The Future of Conversational AI
Looking ahead, conversational AI is becoming more natural and capable:
- More Natural Conversations: AI models are getting better at understanding nuance, emotion, and context. Future bots may even detect user mood (happy, frustrated) via tone or typing patterns and adapt responses.
- Multimodal Interaction: We’ll see more chatbots that handle both text and voice seamlessly. Imagine starting a question by voice at home, continuing it as text on your phone, and later via email – all the same bot.
- Deeper Personalization: As AI learns more about user behavior (with privacy safeguards), bots will give highly personalized answers. Your virtual assistant might know your typical schedule, preferences, or even health metrics to give tailored advice.
- Integration with IoT: Bots will connect more with smart devices. You could tell a home assistant to “make me a cup of tea” and it will coordinate the kettle, the heating system, and the grocery order if supplies run low.
- Local Language Models: Right now, English dominates in AI. But companies worldwide are training models in Chinese, Spanish, Hindi, Arabic, and more. Expect more local-language chatbots that understand slang and cultural context.
- Ethical and Secure AI: As regulation grows, bots will be built with ethics in mind. Transparency (telling users they’re talking to AI, not a human) and data security will be standard.
- Human-AI Collaboration: In many jobs, humans will work alongside chatbots. For instance, doctors might use an AI assistant to summarize patient symptoms, letting the doctor focus on the deeper diagnosis.
Big tech firms continue to invest tens of billions in AI research, including conversational systems.
In practical terms, this means every website and service might soon have some conversational interface. Whether it’s a help chat, a voice command, or even AR/VR interactions, talking to computers will feel very normal.
Conclusion
Conversational AI is transforming how we interact with technology. It brings human-like chat experiences to everyday tasks, making services faster, more engaging, and more efficient. For businesses, it offers 24/7 support, cost savings, and new sales channels. For users, it means getting help in their own words, anytime.
Looking forward, conversational AI will only get smarter. New advances in AI language models and voice tech promise even more natural, helpful conversations. However, ethical design and privacy are crucial as we rely more on these systems.
For readers – whether you’re a tech pro, a marketer, or a curious person – understanding conversational AI is essential. It’s not a buzzword; it’s a core part of modern tech strategy. If you run a business, think about how a chatbot or voice assistant could improve your customer experience. If you’re a user, remember you’re already using this tech every day (maybe without noticing!). And if you’re a developer or student, consider building a simple chatbot – it’s a great way to learn about AI and NLP.
Conversational AI is here to stay. Its changing communication by making technology more human-friendly. We’ve covered the basics and the big picture. The next step is simple: try talking to one today, and experience the future of conversation yourself!
Pingback: Windows 2030: Microsoft's Bold Leap into an AI-First