cryptography and security: The Silent Guardian of Our Digital Lives. In today’s world, we live online. We shop, we bank, and we share information with people all over the planet. Trillions of dollars move through digital systems every single year. But with all this activity, the threats are real.
Hackers and cybercriminals are always trying to find a way in. So, how is your sensitive information kept safe?
Topics Covered
Table of Contents
The answer is cryptography. It’s the essential backbone of secure digital communication and online payments. It’s the silent guardian that ensures only the right people can access your data.
Think of it as a secret language that protects everything you do online. In this guide at hstech.io, we’ll break down
- what it is.
- Where did it come from?
- Why is it more important than ever?
What Is Cryptography and Security?
Simply put, cryptography is the science of keeping information private. It uses clever math to turn a normal message, what we call “plaintext,” into a scrambled mess called “ciphertext.” To do this, it uses a special digital key.
See Also: Boom of Health and Home Technologies: Explore powerful top 5
Ciphertext:
This key is like the password to a secret code. Without the correct key, the ciphertext is just random characters. It’s useless to anyone who might steal it. But with the key, you can instantly turn the ciphertext back into the original message.
For Example, Imagine writing a diary. You use a special cipher to write every word. No one else can read it. That cipher is your cryptography.
This same idea protects bank logins, your medical records, and your favorite online shopping sites. The methods have evolved, but the core concept remains the same: privacy through secrecy. Without it, our digital world would be an open book.
A Quick Journey Through Its History
The idea of hiding messages is very old. It goes back thousands of years. Ancient Egyptians used unusual hieroglyphs to send secret messages. One of the most famous examples comes from Julius Caesar. His “Caesar cipher” was simple. He would just shift every letter in a message by a few places. So, ‘A’ might become ‘D’. It was an effective way to communicate with his generals.
During World War II, a mechanical marvel called the Enigma machine was used by Germany to encrypt military communications.
The real shift to our modern world came in the 1970s. Researchers invented “public-key cryptography.”
Public-key cryptography
This was a massive breakthrough. It meant you no longer needed to meet in person to share a secret key. This invention is what made the secure internet we know today possible. From simple shifts to complex math, cryptography has come a long way.
See Also: NSFW ChatGPT: Top 7 Free Alternatives You Can Try
The Different Types of Cryptography
Cryptography isn’t just one thing. It’s a collection of tools, each with a specific job.
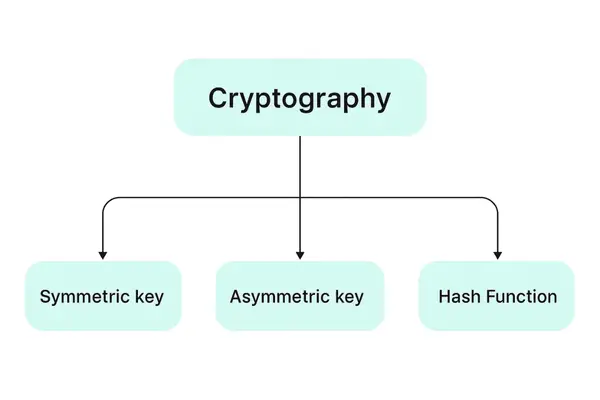
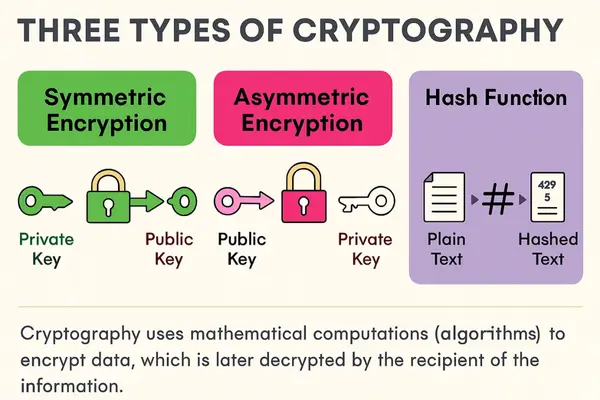
1. Symmetric-Key Cryptography: The Fast and Simple Method
This type is the most straightforward. It uses just one key. The same key is used to both lock and unlock the data. Think of it as a single padlock and a single key. You use the key to lock a box and give a copy to someone else so they can open it.
Symmetric cryptography is very fast. This makes it perfect for encrypting large amounts of data. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a common example.
It is used in things like securing your Wi-Fi network and protecting files on your computer. AES with a 256-bit key is considered incredibly strong.
The only real challenge is safely sharing that single key.
If a hacker intercepts the key, the entire system is at risk.
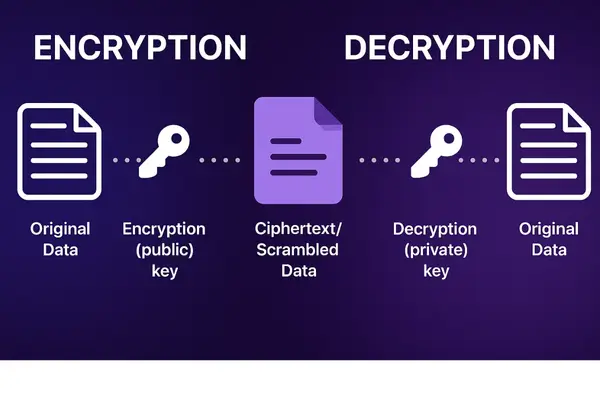
2. Asymmetric-Key Cryptography: The Foundation of Online Trust
This is a more advanced method. This type uses two different keys that are mathematically linked.
- Public key
- Private key
The public key can be shared with anyone. It’s used for encryption. The private key is a secret, and only you have access to it. It’s used for decryption.
Think of it like a public mailbox. Anyone can put a letter in the mailbox, but only you, with your private key, can open the box and read the letter. The public key can’t be used to decrypt the message, which makes it very secure.
This system is the backbone of secure websites. When you see a little padlock icon in your browser and “HTTPS” in the address bar, it means that a secure connection is being used with asymmetric cryptography. This system is slower than symmetric methods, but it’s essential for creating a foundation of trust when you connect to a website for the first time.
3. Hash Functions: The One-Way Lock
This type of cryptography differs in that it doesn’t use a key for decryption. It’s a one-way process. A hash function takes data and turns it into a unique, fixed-size string of characters. This string is called a “hash” or a “digital fingerprint.”
Hash or a Digital fingerprint
If you change even one tiny thing in the original data, the hash changes completely. This makes it perfect for checking data integrity. For example, when you create a password on a website, the site doesn’t store your actual password.
Instead, it stores a hash of your password.
When you log in, it takes the password you enter, hashes it, and checks if the new hash matches the one it has saved. If a hacker steals the website’s database, they get a bunch of useless hashes, not your real password. This technology is also what powers blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
Why Cryptography is Crucial in 2025
By the end of this year, online transactions will likely exceed $28 trillion. Cryptography is the only thing standing between that money and a wave of cybercrime.
The estimated global cost of cybercrime is projected to hit $10.5 trillion annually. Strong cryptography acts as our shield.
It’s about more than just numbers. It’s about trust. People will not use an online service if they feel their information is at risk. Cryptography gives users confidence.
Tokenization
It ensures that when you enter your credit card details, they are converted into a secure code. It uses methods like “tokenization” to replace sensitive data with a unique, meaningless token. This is a powerful defense against data breaches.
The majority of all online transactions use these kinds of protections. Businesses that follow these security standards not only protect their customers but also avoid massive fines and reputational damage. Cryptography is what allows the global digital economy to function smoothly and safely.
Protecting Your Conversations and Data
Privacy in communication is just as important as security in payments. Cryptography ensures that your private conversations stay private. Most modern messaging apps use something called “end-to-end encryption.”
End-to-end Encryption
This means that your messages are encrypted on your device and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device. No one, not even the company that owns the app, can read our messages. It uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography to make this happen seamlessly.
In the business world, tools like VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) utilize encryption to secure corporate data. This is especially important with the rise of remote work. It prevents hackers from eavesdropping on sensitive meetings or files.
Strong cryptography also protects against “man-in-the-middle” attacks, where a hacker tries to intercept and alter data. Digital signatures, powered by cryptography, verify that a message or file is truly from the person it claims to be from.
How Your Online Payments Stay Safe
When you make a payment online, a whole chain of cryptographic events happens in a flash.
- Data is Encrypted: The moment you hit “pay,” your credit card number is encrypted. This is often done using a fast symmetric algorithm like AES. It turns your card number into a secure code before it even leaves your device.
- A Secure Tunnel is Opened: Your browser uses asymmetric cryptography to set up a secure channel with the website’s server. This channel is called a TLS (Transport Layer Security) connection. It’s the digital equivalent of a secure, locked tunnel.
- Authentication Happens: The merchant’s public key is used to verify their identity. This proves that you are sending your information to the real store, not to a fake, phishing site.
- Integrity is checked: Hash functions are used to create a digital fingerprint of the transaction details, like the amount. This ensures that no one has tampered with the payment amount while it was in transit.
- Tokenization Adds an Extra Layer: Often, your real card information is never even processed. A unique token replaces it. The token can only be used for that specific transaction. This means if a hacker gets hold of the data, all they get is a meaningless string of characters.
This multi-layered approach is why mobile wallets and cryptocurrencies are so secure. It’s all built on a robust foundation of cryptography.
More Than Just Money: Everyday Uses
Cryptography is everywhere. We just don’t always see it. In the healthcare industry, it is required to secure patient records. This keeps your private health information confidential and in compliance with strict privacy laws.
In the world of supply chain management, blockchain technology uses cryptographic hashes to create a tamper-proof record of every item’s journey. This builds trust and transparency.
Your smart home digital devices, like smart locks and security cameras, also use encryption. This ensures that commands you send to them are secure and can’t be intercepted by a hacker. Even digital rights management (DRM) for movies and music uses cryptography to prevent unauthorized copying. Governments rely on it for classified communications. Cryptography is an integral part of our modern lives.
The Big Benefits of Strong Cryptography
- Privacy: It is the single most important tool for keeping your data private.
- Authenticity: It helps you verify that a message or file is truly from the source it claims to be from.
- Integrity: It ensures that data has not been changed or altered while being sent.
- Fraud Reduction: By making it much harder to steal and misuse information, it directly reduces financial fraud.
- Consumer Confidence: It builds the necessary trust for people to engage in online commerce and communication. A majority of shoppers will leave a site if they don’t feel it’s secure.
The Challenges We Face
Even with all its power, cryptography isn’t perfect. We face some very real challenges.
1. Key Management:
This is a big one. It’s a simple problem with a difficult solution. If a private key is lost or stolen, the data it protects can be lost forever or accessed by a hacker. Storing these keys securely is a constant struggle. Solutions like hardware security modules (HSMs) are used to store keys in a highly secure way.
2. The Quantum Threat:
This is perhaps the biggest challenge on the horizon. The quantum computers of the future will be so powerful that they could potentially break our current encryption standards, like RSA. At the same time, this isn’t an immediate threat.
We need new types of algorithms that can resist these quantum attacks. This is called “post-quantum cryptography,” and it’s a major area of research right now.
3. Human Error:
The biggest weakness in any system is often human error. Even the strongest cryptographic algorithm can be useless if it’s implemented incorrectly. Poor coding or bad security practices can expose weaknesses. This is why proper training and regular security audits are so important.
See Also: Shocking AI Dominance in 5 years: Envision a Shrinking World
What’s Next for Cryptography?
The field of cryptography is always moving forward. Researchers are constantly working on new solutions to stay ahead of the threats.
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC):
The development of new algorithms that are safe from quantum computers is a top priority.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
This is a fascinating new area. It’s a way to prove that you know something without revealing the actual information. For example, you could prove you have enough money in your account to purchase without revealing your exact balance.
This will have a massive impact on digital privacy.
Homomorphic Encryption:
This technology enables computers to perform algorithmic calculations on encrypted data without decrypting it. Imagine being able to analyze data in the cloud without anyone, not even the cloud provider, being able to see what the data is.
Biometric Integration:
We’ll see more encryption keys tied to fingerprints, facial scans, or other biometric data. This makes things more user-friendly and secure.
Your Takeaway
Cryptography is not just a technical term for experts. It is the fundamental technology. It is what keeps
- Your Money safe,
- Your conversations are private,
- Your data is secure.
As we move further into the digital age, with new technologies and new threats emerging, the science of cryptography will continue to evolve and remain the essential guardian of our online lives.
Read also: 12 Gadgets for Teen: Revolutionize with Cool Tech and Futuristic Toys,
The Bright Future of AI Agents: Learning, Adapting, and Innovating in 2025