Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has changed the way devices interact with each other. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT connects billions of devices worldwide. But as this ecosystem grows, a major challenge arises: how can different IoT systems communicate seamlessly?
Topics
Table of Contents
This is where Inter-IoT comes in. It’s an approach that focuses on interoperability—the ability of devices, networks, and platforms to connect and work together, no matter who built them.
In this pillar guide, we’ll cover:
- What Inter-IoT means
- How it works
- Why interoperability is crucial
- Real-world use cases
- Benefits, challenges, and the future of Inter-IoT
What is Inter-IoT?
Inter-IoT stands for Interoperability of Internet of Things systems. It is not a single technology but a framework and set of methodologies that enable different IoT platforms, networks, and devices to communicate and share data.
In simple terms:
- IoT connects devices within a network.
- Inter-IoT connects multiple IoT ecosystems with each other.
This ensures that a smart home, smart city, healthcare system, or industrial IoT solution can interact without barriers.
Industrial IoT and Healthcare IoT Explained: 7 Key Benefits
Why Do We Need Inter-IoT?
The IoT market is booming, with over 30 billion devices expected by 2030. But there’s a big problem: most IoT systems work in silos.
- A smart fridge from Samsung can’t easily talk to a smart thermostat from Google.
- A hospital’s IoT monitoring system may not share data with city emergency networks.
- Industrial IoT machines often run on proprietary platforms, limiting collaboration.
Without interoperability, IoT remains fragmented and less useful. Inter-IoT solves this by building bridges across IoT ecosystems.
How Does It Work?
Inter-IoT uses a layered architecture to connect different IoT platforms. Let’s break it down:
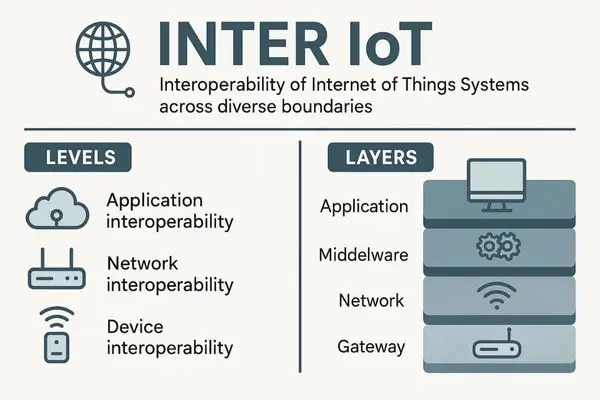
1. Device Layer
Includes sensors, wearables, machines, vehicles, and other physical devices. It enables communication between different types of devices, such as sensors, cameras, and GPS units, even if they use different protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LoRa. Handles protocols, data formats, and device drivers.
Example: Industrial robots and IoT sensors with different firmware can be connected.
2. Network Layer
Handles connectivity (Wi-Fi, 5G, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, Bluetooth, etc.). It allows different communication networks and gateways to exchange data securely and efficiently, supporting the mobility of connected devices. Ensures connectivity across different communication technologies (Wi-Fi, ZigBee, 5G, Bluetooth).
Example: Smart city sensors using different networks can still communicate in a unified way.
3. Middleware Layer
Provides a common “translation” platform so different IoT systems can understand each other. It facilitates the reuse and exchange of services, such as alerts, dashboards, and data analytics tools, across different IoT platforms. Connects IoT devices and services using APIs, data models, and semantic translators.
Example: Data from smart meters can be translated into formats usable by energy management systems.
4. Application Layer or Plateform level
Where end-users interact with IoT (apps, dashboards, analytics). The framework connects different cloud platforms (like AWS IoT or Microsoft Azure IoT) so that applications built on one platform can use data from another. Ensures apps built on one IoT platform can communicate with apps on another.
Example: A healthcare monitoring app can integrate data from wearable fitness trackers.
5. Interoperability Layer
The core of Inter-IoT. It manages:
- Protocol translation
- Data standardization
- Security and authentication
- API communication
Example: A wearable fitness tracker can send heart rate data to a hospital’s IoT platform, which then communicates with city emergency services if a patient’s health data shows risk.
A common, shared “ontology” is used to provide a shared interpretation of data, ensuring that different systems understand the meaning and context of the information they exchange. Benefits and applications
Key Features
- Cross-platform communication: Devices from different vendors connect smoothly.
- Scalability: Supports billions of devices without breaking.
- Security-first approach: Ensures encrypted and trusted data sharing.
- Flexibility: Works across industries like healthcare, smart cities, and manufacturing.
- Real-time processing: Ensures instant data flow between systems.
Real-World Applications
Here are some practical examples where Inter-IoT makes a difference:
1. Healthcare
- Patient wearables share data with hospitals.
- Hospitals connect with ambulance networks.
- Emergency responders get instant alerts.
2. Smart Cities
- Traffic sensors, public transport, and emergency services share information.
- Better traffic management, reduced congestion, and faster emergency response.
3. Industrial IoT
- Machines from different manufacturers work together on factory floors.
- Predictive maintenance improves efficiency.
4. Smart Homes
- Connects smart appliances, lighting, and energy systems from different brands.
- Users manage everything in one interface.
5. Logistics & Transportation
- Shipment trackers communicate with port systems, warehouses, and delivery networks.
- Enables faster and safer supply chain management.
Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Seamless communication | Devices and platforms share data without silos. |
| Reduced costs | Cuts integration and maintenance costs. |
| Faster innovation | Developers build apps across multiple platforms. |
| Better decision-making | Unified data leads to stronger insights. |
| Scalability | Supports future device growth. |
| User satisfaction | Smooth experiences across devices and apps. |
Seamless Connectivity Devices from multiple brands and platforms work together.
Improved Efficiency Reduced manual integration and better automation.
Cost Reduction Less need for proprietary systems.
Enhanced Security Unified frameworks improve trust and safety.
Scalability Can grow with the IoT ecosystem.
Challenges of Inter-IoT
Even though Inter-IoT is powerful, it faces obstacles:
- Lack of Standards – Different vendors use different communication protocols.
- Security Risks – More connections mean more vulnerabilities.
- High Integration Costs – Businesses need investment to connect systems.
- Data Privacy Issues – Sharing data across systems raises privacy concerns.
- Complex Implementation – Requires advanced middleware and expertise.
The Future of Inter-IoT
Experts believe Inter-IoT will be the backbone of the next digital revolution. Key trends shaping the future include:
- AI-driven IoT: Smarter decision-making across platforms.
- 5G & 6G networks: Faster connectivity, real-time data sharing.
- Blockchain-based security: Trustless and transparent interoperability.
- Edge Computing: Processing closer to devices for instant responses.
- Universal Standards: Industry-wide adoption of shared frameworks.
By 2035, Inter-IoT could power autonomous cities, global healthcare systems, and fully integrated industries.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between IoT and Inter-IoT?
- IoT connects devices within one system.
- Inter-IoT connects multiple IoT systems together.
Q2. Is Inter-IoT already in use?
Yes. Many smart city projects, healthcare systems, and industrial setups are testing Inter-IoT solutions.
Q3. How does Inter-IoT improve security?
By standardizing authentication, encryption, and data handling across platforms.
Q4. Which industries benefit most from Inter-IoT?
Healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and smart cities.
Conclusion
Inter-IoT is the next big step in the Internet of Things journey. It solves the problem of fragmentation by enabling seamless communication across devices, platforms, and networks.
From healthcare to smart cities and logistics, its potential is huge. Businesses that adopt this advanced technology early will benefit from better efficiency, security, and scalability.
As technology advances with AI, blockchain, and 5G, Inter-IoT will become the foundation of a truly connected world. For more detail about iot visit oracle.com
Pingback: Withings ScanWatch 2 Update: Powerful 35-Day Battery + AI Features
Pingback: Top 5 Inter-IoT challenges: Powering Smart Cities and Amazing Future Trends